Emergency Cases
Salamanca Guanajuato
464 116 2012
San Miguel de Allende
415 111 6819
Please contact in case of emergency or to request a consultation.
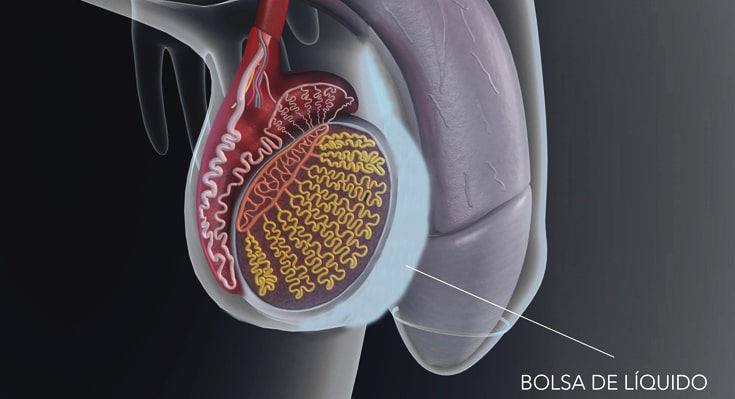
A hydrocele is a swelling of the scrotum that occurs when fluid builds up in the thin lining that surrounds the testicle. Hydrocele is very common in new borns and usually disappears on its own by one year of life. However, older boys and adult men can also develop a hydrocele due to swelling or injury within the scrotum.
Hydrocele cannot be prevented in the case of newborn babies since it is an alteration in anatomical development. Therefore, it is important to visit the pediatrician and the urologist to follow its evolution.
In case of adults, its appearance could be prevented or partially avoided, all this by avoiding activities that favor testicular microtauma.
For adolescent and adult males the best protection against a hydrocele is to keep the testicles and scrotum free from injury by wearing proper padding and tight-fitting undergarments, if you participate in contact sports or work in activities that carry a risk of concussion.

Generally, the hydrocele, once it is stablished, does not usually disappear unless it is secondary to inflammation and appears simultaneously, in which case this hydrocele is considered reactive and may decrease or disappear when the inflammation subsides.
A hydrocele is usually not painful or harmful and may not need any treatment. How ever if you have swelling in your scrotum, see you doctor to rule out other causes.
Hydrocele can be:
Congenital:
It is generated by the passage of fluid from the interior of the abdomen to the scrotum through a small communication, which has not been completely closed during the development of the fetus. This type is the most common and is also called a communicating hydrocele. Within this type, there is also a non-communicating hydrocele, which arises when the communication between the abdomen and the scrotum closes complete, but fluid remains trapped inside. If this fluid is retained in the inguinal region (rather than in the scrotum), it is called a cord cyst.
Acquired:
This type of hydrocele usually manifest during adolescence, is cause by excess fluid production or lack of reabsorption of it, by the covers surrounding the testicle and is also called non-communicating hydrocele.
Diagnosis is usually made by examining the scrotum, wich may appear enlarged, it usually painless and often has a rubbery consistency.
As part of the examen, a light is usually shined behind each testicle (Transillumination) to look for solid masses that may caused by other problems, such as testicular cancer.
However, due to technical advances and the great advantages that ultrasound gives, it has become the main tool for diagnosis this condition and it is through ultrasound examination that hydrocele can be diagnosed, accurately quantified, and rule out complications and injuries to the testicle and its adjacent structures
The hydrocele does not usually produce symptoms unless it is great volume, In this case, the symptoms could be:


Please contact in case of emergency or to request a consultation.