Infertility is a problem that affects many couples worldwide, and it is estimated that approximately 15% of couples have difficulty conceiving. While infertility has traditionally been associated more with women, male fertility problems have also been shown to be a significant cause of inability to conceive.
In this article, we will explore what male infertility is, examine some of the underlying causes,
and discuss the different treatments available.
What is male infertility?
Male infertility is defined as the inability of a man to achieve pregnancy in a fertile partner after one year of unprotected intercourse.
It can be due to a number of factors, including problems with sperm production, transport or quality.
Infertile men may have a low sperm count, poor sperm motility or abnormal sperm morphology, which makes it difficult for the sperm to reach the egg and fertilize it.

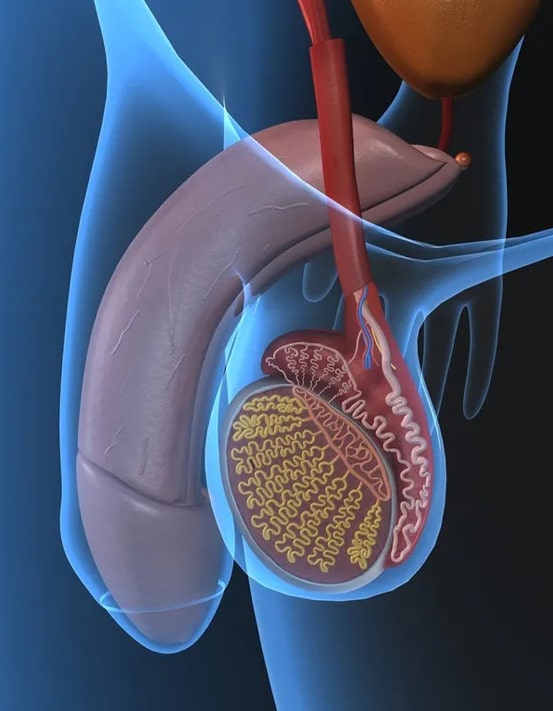
Causes of male infertility:
Genetic and congenital factors:
Some men may have genetic abnormalities that affect sperm production or function, such as Klinefelter’s syndrome or Y chromosome microdeletion.
Hormonal disorders:
Hormonal imbalances, such as low testosterone levels or high prolactin levels, can affect sperm production.
Varicocele:
Varicocele is a dilation of the veins in the scrotum, which can increase the temperature of the testicular area and affect sperm quality.
Infections:
Genital tract infections, such as epididymitis or prostatitis, can cause damage to the seminal ducts and reduce male fertility.
Lifestyle and environmental factors:
Factors such as tobacco use, excessive alcohol consumption, recreational drug use, obesity, and exposure to toxic chemicals can adversely affect sperm quality.
Male infertility treatments:
Medications:
Some medications can help improve sperm production, correct hormonal imbalances or treat infections that affect male fertility.
Surgery:
In cases of varicocele, obstructions or blockages in the seminal ducts, surgery may be an option to restore fertility.
Assisted Reproductive Techniques (ART):
In more complex cases of male infertility, techniques such as intrauterine insemination (IUI) or in vitro fertilization (IVF) may be considered.
These techniques involve manipulation of sperm and eggs outside the body to facilitate conception.
IUI involves placing selected sperm directly into the uterus, while IVF involves fertilizing eggs in the laboratory and transferring embryos into the uterus.
Assisted reproduction with sperm microinjection (ICSI):
This technique is used when there are severe problems with sperm quality.
It consists of directly injecting a sperm into a mature egg to achieve fertilization.
Sperm donation:
In cases where it is not possible to use the man’s own sperm, either due to insufficient sperm production or total absence of sperm, sperm donation may be an option.
Sperm from an anonymous donor is used to fertilize the female partner’s eggs.
Genetic counseling:
In certain cases where underlying genetic problems are detected, genetic counseling and prenatal testing may be recommended to help prevent the transmission of genetic disorders to offspring.
It is important to note that appropriate treatment will depend on the underlying cause of male infertility and the individual circumstances of each couple.
Therefore, it is essential to seek the guidance and diagnosis of a fertility specialist or urologist.