Emergency Cases
Salamanca Guanajuato
464 116 2012
San Miguel de Allende
415 111 6819
Please contact in case of emergency or to request a consultation.
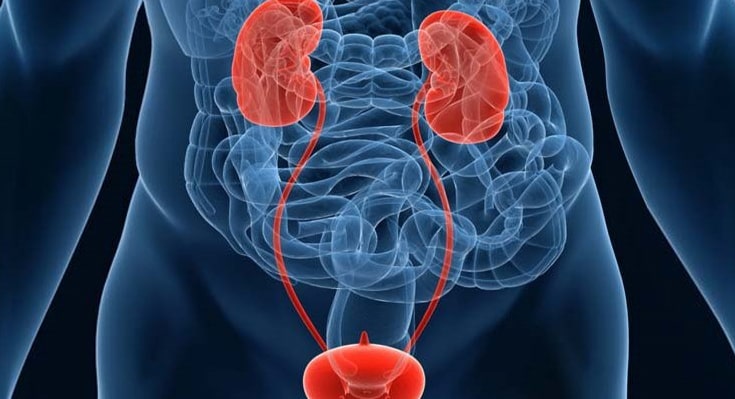
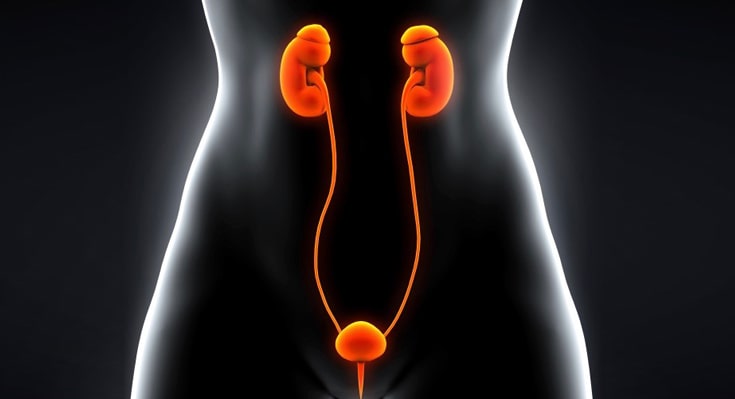
Urinary tract infections are infections that develop in any part of the urinary system; the kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra.
Most infections are found in the lower urinary tract ( the bladder and urethra).
This infection is usually associated with bacteriuria and pyuria.
Bacteriuria is the presence of bacteria in the urine, which under normal conditions are not found there and it is a valid indicator of colonization and/or infection.
It can be symptomatic or asymptomatic. Kidney infection (pyelonephritis) is another type of urinary tract infection and is less common than bladder infection, but it is more serious.

Doctors usually treat urinary tract infections with antibiotics. However, steps can be taken to reduce the chances of getting urinary tract infections. Being women who have a higher risk of contracting a urinary tract infection than men.
The infection when limited to the bladder can be painful and uncomfortable. However, if the infection spreads to the kidney, the consequences can be much more serious. Urinary tract infections are classified into:
Uncomplicated urinary tract infection:
It is the infection that affects a healthy patient with normal urinary tract from the anatomical and functional point of view.
Complicated urinary infection:
It is associated with factor that increase the probability of entry of bacteria and reduce the effectiveness of treatment.
First infection or isolated infection:
It is the one presented by an individual who has never had a urinary tract infection before or who had an infection a long time ago. The term reinfection describes a new event associated with the reintroduction of bacteria into the urinary tract from the outside.
Bacterial persistence:
It is the recurring infection caused by the same bacteria that return to the urinary tract from a focus within them, such as an infectious stone or the prostate.
Bacterial urinary tract infections are the most frequent, since these generate around 7 million consultations per year.
According to studies, 30% of women will have developed a symptomatic infection in their first 24 years. And 20% of women and 10 % of men will have urinary tract infections after the age of 65.
Urinary tract infections don´t always cause signs and symptoms, but when they do, they can include:
Please contact in case of emergency or to request a consultation.