Glomerulonephritis is a kidney disease that affects the glomeruli, essential structures in the filtering function of the kidneys.
It is characterized by inflammation of these small blood vessels, which can result in kidney damage and other symptoms.
In this article, we will explore in detail what is glomerulonephritis, its causes, symptoms,
diagnosis, treatments and how to prevent it.
Join us on this tour of this kidney condition!

What is Glomerulonephritis?
Glomerulonephritis is a kidney disease that occurs due to inflammation of the glomeruli, which are the structures responsible for filtering waste and excess fluids from the blood. These small blood vessels are found in the kidneys and are vital for maintaining the proper balance of fluids and chemicals in the body.
When the glomeruli become inflamed, their filtering ability is compromised, which can lead to the accumulation of waste products and fluids in the body.
Causes of glomerulonephritis
There are several causes of glomerulonephritis, and these can vary depending on the type of disease. Some of the most common causes include:
Bacterial infections:
Certain bacterial infections, such as streptococcal infection of the throat or skin, can trigger post-infectious glomerulonephritis. In this case, the immune system response to the infection causes inflammation of the glomeruli.
Autoimmune diseases:
Conditions such as systemic lupus erythematosus and vasculitis can cause glomerulonephritis. In these cases, the immune system attacks healthy body tissues, including the glomeruli.
Use of medications:
Certain medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or antibiotics, can cause adverse reactions in the kidneys and result in glomerulonephritis.
Inherited diseases:
Some forms of glomerulonephritis are inherited and are passed down through families. Examples of these diseases include Alport disease and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis.
It is important to keep in mind that these are only some of the possible causes of glomerulonephritis, and each case may be unique. Consultation with a medical specialist is essential to determine the specific cause and appropriate treatment.
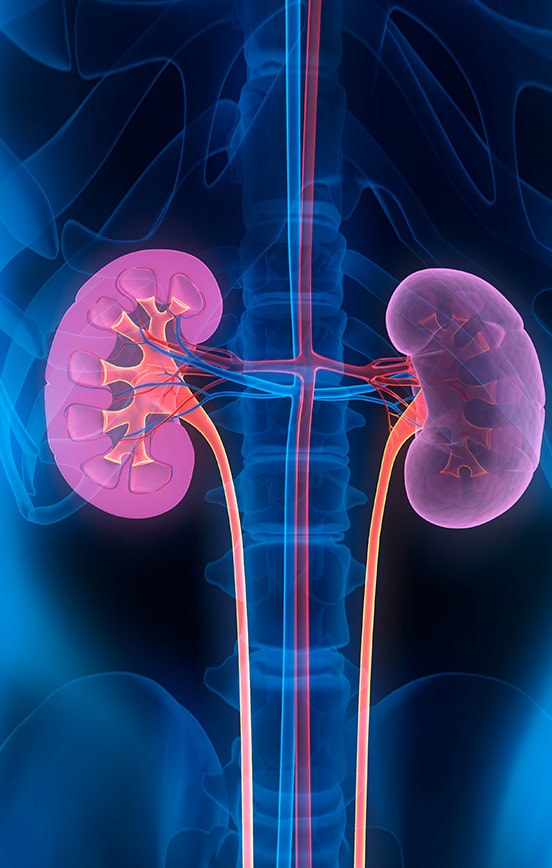
Symptoms of Glomerulonephritis
Symptoms of glomerulonephritis can vary depending on the severity and type of disease.
Some of the most common symptoms include:
-Presence of blood in the urine (hematuria).
-Foamy urine due to the presence of protein (proteinuria)
-Swelling in the body, especially in the ankles and around the eyes (edema)
-Fatigue and weakness
-High blood pressure
-Low back pain or tenderness
-Frequent urination, especially at night (nocturia)
It is important to note that these symptoms may vary in each individual and not all patients have all of the above symptoms.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is essential to consult a physician for an accurate diagnosis.
Diagnosis of Glomerulonephritis
The diagnosis of glomerulonephritis is usually made by a combination of blood tests, urinalysis and imaging tests. These are some of the methods used to diagnose this disease:
Blood Tests
Blood tests may reveal the presence of high levels of creatinine and urea in the blood, indicating decreased kidney function. In addition, tests can be performed to detect the presence of specific antibodies that may be related to glomerulonephritis.
Urinalysis
Urinalysis is a key tool in the diagnosis of glomerulonephritis. The presence of blood and protein in the urine, as well as microscopic analysis of cells and sediment, can provide important information about the status of the glomeruli.
Renal Biopsy
In some cases, it may be necessary to perform a renal biopsy to obtain a sample of kidney tissue and examine it under a microscope. This test allows the specific cause of the glomerulonephritis to be determined and the degree of kidney damage to be assessed.
It is important to remember that an accurate diagnosis of glomerulonephritis must be made by a physician specializing in nephrology or urology.
Treatment of glomerulonephritis
Treatment of glomerulonephritis is based on the underlying cause of the disease and the degree of kidney damage.
Some common treatment options include:
Medications:
Depending on the cause of glomerulonephritis, medications may be prescribed to control inflammation, suppress the immune system, or treat concomitant infections.
Dietary changes:
In some cases, a low-salt, low-protein diet may be recommended to reduce the workload on the kidneys and control blood pressure.
Dialysis:
In severe cases of glomerulonephritis, when kidney function is severely compromised, dialysis may be necessary to remove accumulated wastes and fluids from the body.
Renal transplantation:
In cases of irreversible renal damage, kidney transplantation may be an option to consider.
However, this procedure requires a thorough evaluation and the use of lifelong immunosuppressive medications.
It is essential to follow the recommendations and treatment guidelines established by the specialist physician.
Each case of glomerulonephritis is unique, and the appropriate treatment may vary depending on the cause and stage of the disease.
Prevention of Glomerulonephritis
Although it is not always possible to prevent glomerulonephritis, there are measures that can help reduce the risk of developing this disease.
Some recommendations for prevention include:
Maintain good hygiene:
Avoiding bacterial infections, especially those related to the throat and skin, can help prevent post-infectious glomerulonephritis.
Regular hand washing and following proper personal hygiene practices are essential.
Control autoimmune diseases:
If you have an autoimmune disease, such as lupus, it is important to follow your doctor’s recommendations to properly manage it and reduce the risk of kidney complications.
Use medications with caution:
It is important to follow medical advice when taking medications, especially those that may have adverse effects on the kidneys.
Always inform your doctor about any medications you are taking.
Maintain a healthy lifestyle:
Eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly and maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce the risk of developing kidney disease, including glomerulonephritis.
Remember that these preventive measures can help reduce risk, but they do not guarantee total prevention of glomerulonephritis.
If you have kidney-related concerns or symptoms, it is critical to seek appropriate medical attention.

Conclusion
If you have concerns or symptoms related to your kidneys, do not hesitate to consult a medical specialist.
Remember that prevention and proper management can help you lead a healthy life despite glomerulonephritis.
It is very important that this diagnosis is made by a specialist Urologist like Dr. Moises Vidal.
For more information make an appointment and request a consultation.