Glomerulosclerosis is a chronic kidney disease that affects the glomeruli, fundamental structures
for the proper functioning of the kidneys.
What is Glomerulosclerosis?
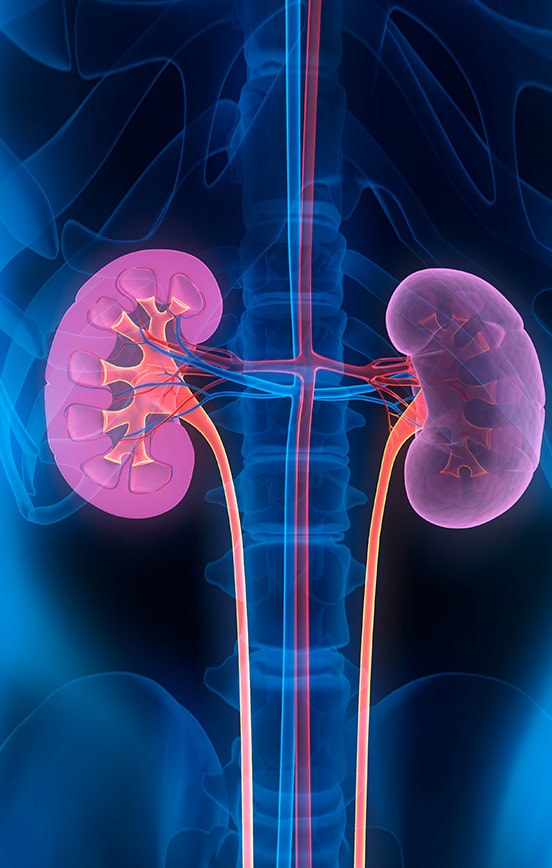
The glomeruli are responsible for filtering the blood and removing waste and excess fluid from the body.
When glomerulosclerosis develops, the glomeruli become hardened and scarred, which interferes with their ability to filter properly.
As a result, kidney function is compromised and can lead to serious health problems.

Causes of Glomerulosclerosis
Glomerulosclerosis can have a variety of causes, including:
Diabetes:
Diabetes is one of the main causes of glomerulosclerosis.
High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels in the kidneys, including the glomeruli, leading to their hardening and scarring.
High blood pressure:
High blood pressure can put excessive strain on the blood vessels of the kidneys, affecting the function of the glomeruli and leading to glomerulosclerosis.
Autoimmune diseases:
Some autoimmune diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus, can cause inflammation and damage to the kidneys, increasing the risk of developing glomerulosclerosis.
Obesity:
Excess weight and obesity are associated with an increased risk of glomerulosclerosis, possibly due to the additional pressure placed on the kidneys.
Long-term use of certain medications:
Some medications, such as nonsteroidal painkillers and drugs to treat HIV, can damage the kidneys over the long term and contribute to the development of glomerulosclerosis.
Symptoms of glomerulosclerosis
Glomerulosclerosis may be asymptomatic in the early stages and symptoms may vary depending on the severity of the disease.
Some possible symptoms of glomerulosclerosis include:
-Presence of protein in the urine (proteinuria).
-Swelling in the body, especially in the legs and the area around the eyes (edema).
-High blood pressure (hypertension).
-Fatigue and weakness.
-Changes in urination, such as increased or decreased urinary frequency.
It is important to note that these symptoms may also be present in other health conditions, so it is essential to consult a physician for an accurate diagnosis.
Diagnosis of Glomerulosclerosis
To diagnose glomerulosclerosis, several examinations and tests can be performed, including:
Urinalysis:
A urine sample is examined for the presence of protein and other indicators of kidney damage.
Blood tests:
Kidney function is assessed by measuring creatinine and urea levels in the blood.
Kidney biopsy:
A small sample of kidney tissue is removed for examination under a microscope to confirm the diagnosis of glomerulosclerosis.
Imaging studies:
Imaging techniques, such as ultrasound or MRI, may be used to evaluate the structure and function of the kidneys.
Treatment of glomerulosclerosis
Treatment of glomerulosclerosis is aimed at controlling symptoms, slowing disease progression, and protecting kidney function. Treatment options may include:
Medications:
Medications may be prescribed to control blood pressure, reduce inflammation and decrease the amount of protein in the urine.
Lifestyle changes:
Adopting healthy lifestyle habits, such as eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly and avoiding alcohol and tobacco use, can help maintain kidney health.
Dialysis:
In cases of severe kidney failure, dialysis may be necessary to replace kidney function.
Kidney transplantation:
For patients with end-stage kidney failure, a kidney transplant may be a long-term treatment option.
It is essential to follow medical recommendations and regular follow-up to control the disease and prevent complications.


Conclusion
Glomerulosclerosis is a chronic kidney disease that affects the glomeruli and can have a significant impact on kidney health.
It is important to seek medical attention if symptoms such as proteinuria, edema, or high blood pressure are present.
With early diagnosis and proper treatment, it is possible to control the disease and preserve kidney function.
Adopting a healthy lifestyle and following medical recommendations are key steps in dealing with glomerulosclerosis
and promoting good kidney health.
It is very important that this diagnosis is made by a specialist Urologist such as the Dr. Moises Vidal.
For more information make an appointment and request a consultation.