Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (HUS) is a rare but serious disease that affects the renal system.
Also known as Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (HUS), this disorder can have serious health consequences
if not diagnosed and treated early.
In this article, we will explore in detail what Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome is, its causes,
symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and prevention.
Join us in this journey through a disorder that requires immediate medical attention to avoid major complications.
What is Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome.
Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome is a disease characterized by a combination of acute renal failure, hemolytic anemia (abnormal destruction of red blood cells) and thrombocytopenia (decrease in the number of platelets in the blood). Although it can affect people of all ages, it is most common in young children, especially those under 5 years of age. HUS can be triggered by different factors, with infection by Escherichia coli (E. coli) bacteria being the most common cause in children.
Causes of Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome.
The main trigger for Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome is infection with Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) bacteria. This bacterium is commonly found in the intestinal tract of animals such as cattle and sheep, and can contaminate food and water. Infection can occur from eating raw or undercooked food, especially contaminated beef, or drinking untreated water. Other less common causes of HUS include infections by other Shiga toxin-producing bacteria, as well as certain medications and genetic disorders.
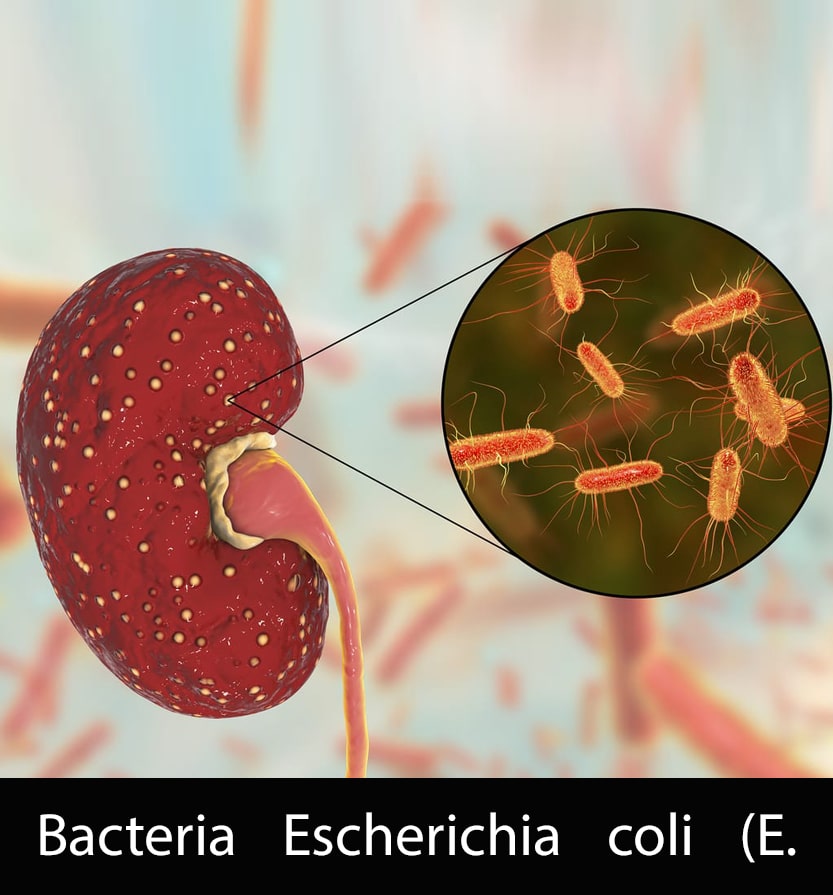
Symptoms of Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome.
Symptoms of HUS can vary in severity and may include:
-Bloody diarrhea.
abdominal pain
-Vomiting.
-Fatigue and weakness.
-Pallor.
irritability in children
-Decreased urine production.
-Swelling in the body, especially in the face, hands and feet.
-Bleeding from the nose or gums.
It is important to note that symptoms may manifest differently in children and adults. In some cases, HUS can lead to the development of serious complications, such as chronic kidney failure, neurological damage and central nervous system disorders.
Diagnosis of Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome..
If HUS is suspected, it is critical to seek immediate medical attention. The physician will perform a complete evaluation of the patient, taking into account the presenting symptoms and medical history. To confirm the diagnosis, the following studies may be performed:
Blood and urine tests.
Blood and urine tests will be performed to evaluate kidney function, as well as the presence of anemia and thrombocytopenia. These tests may include red blood cell and platelet counts, kidney function tests, and specific tests for E. coli bacteria.
Stool culture.
A stool culture may be performed to identify the presence of Shiga toxin-producing E. coli bacteria or other HUS-causing bacteria.
Imaging studies.
In some cases, imaging studies, such as a renal ultrasound, may be performed to evaluate the condition of the kidneys and to rule out other possible causes of symptoms.
Treatment of Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome.
Treatment of HUS focuses on relieving symptoms, preventing complications, and supporting the kidneys during the recovery process.
Treatment measures may include:
-Bed rest.
-Adequate hydration to maintain fluid and electrolyte balance in the body.
-Blood transfusions in cases of severe anemia.
-Medications to control blood pressure and reduce swelling.
-Dialysis or hemofiltration in cases of severe renal failure.
It is important to note that the treatment of Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome should be supervised by a specialized medical team, as each case may require individualized therapeutic approaches.
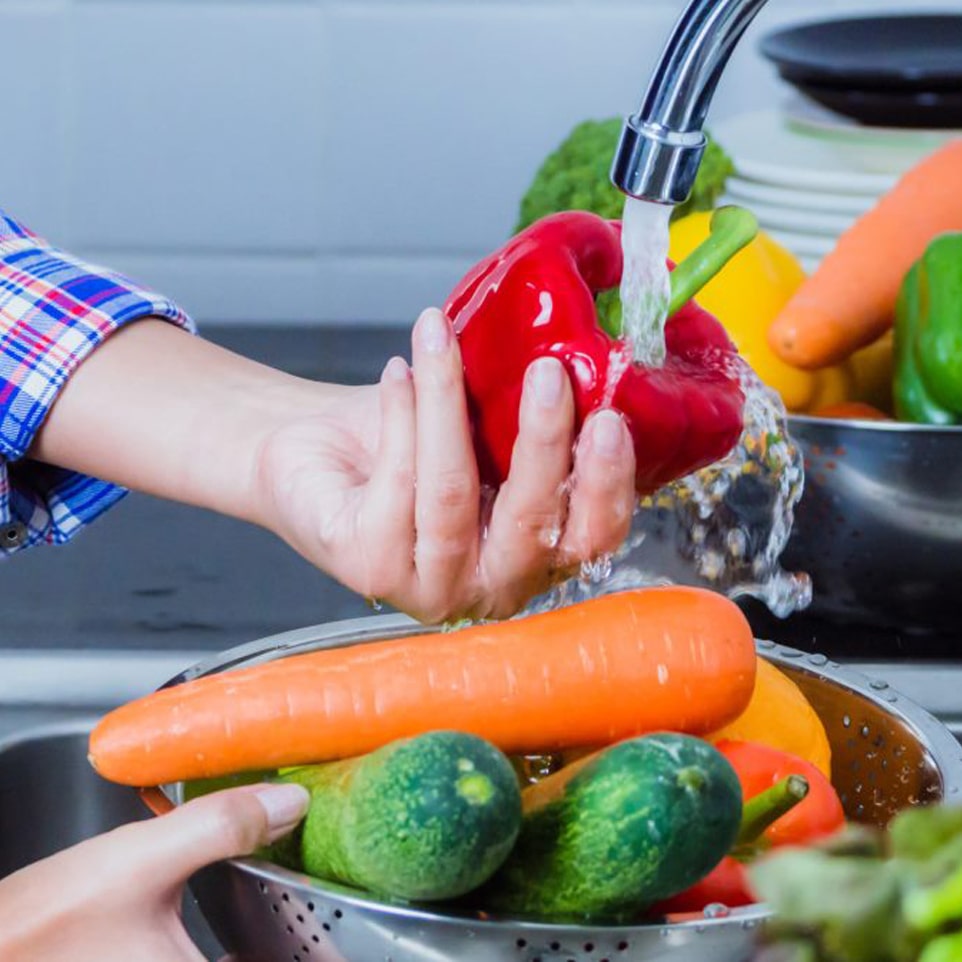

Prevention of Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome.
Since infection by E. coli bacteria is one of the main causes of Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome, it is essential to take preventive measures to reduce the risk of contracting the disease.
Some recommendations include:
-Proper hand washing before eating and preparing food.
-Cooking food at safe temperatures to kill bacteria.
-Avoid consuming raw or undercooked meat.
-Using potable or treated water for drinking and washing food.
-Wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly before eating them.
It is important to educate children about the importance of personal hygiene and food safety to prevent infection and illness.
Conclusion
Hemolytic uremic syndrome is a serious disorder of the renal system that requires immediate medical attention. Shiga toxin-producing E. coli bacteria are the main cause of this disease, especially in children. Knowing the symptoms, seeking early medical attention and following preventive measures can help prevent HUS and its complications. Remember the importance of personal hygiene, food safety and food education to protect your health and the health of your loved ones.
It is very important that this diagnosis is made by a specialist Urologist such as the Dr. Moises Vidal.
For more information make an appointment and request a consultation.